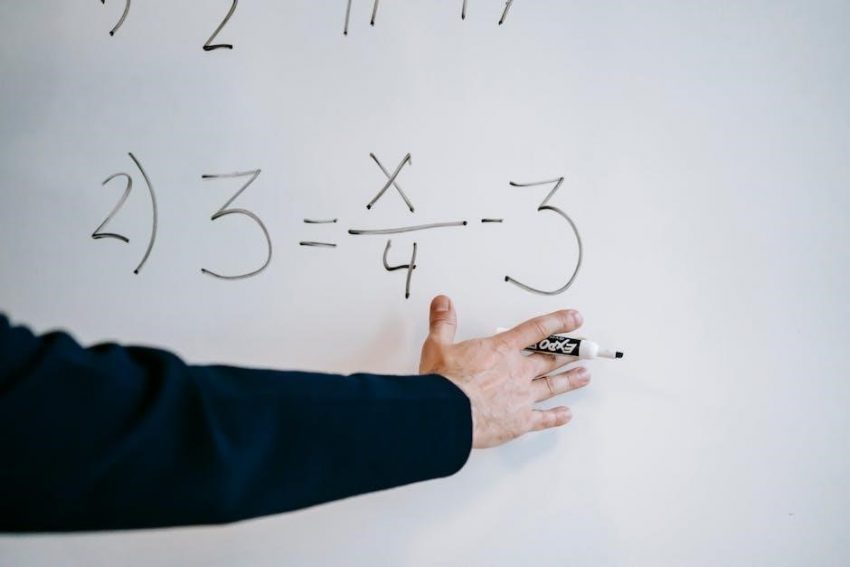One-step equations are fundamental building blocks in algebra, offering a gentle introduction to the world of equation solving.
Mastering these equations provides a solid foundation for tackling more complex mathematical challenges encountered in higher-level courses.
Printable PDF worksheets and online tutorials are readily available to support learning and practice, enhancing comprehension and skill development.
What are One-Step Equations?
One-step equations are algebraic equations that require only one operation to isolate the variable and find its value. These equations typically involve a single variable, a constant, and one arithmetic operation – addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division. They represent a basic level of algebraic problem-solving, serving as a crucial stepping stone to more complex equations.
Essentially, a one-step equation presents a mathematical statement where the goal is to “undo” a single operation performed on the variable. For instance, an equation like x + 5 = 10 requires only one step – subtracting 5 from both sides – to solve for x. Resources like solving one-step equations PDF worksheets provide structured practice.
These equations are foundational because they emphasize the core principle of maintaining balance in an equation: whatever operation is performed on one side must also be performed on the other to preserve equality. Understanding this principle is vital for success in algebra and beyond.
Why are they Important?
One-step equations are incredibly important as they form the bedrock of algebraic thinking. Mastering them builds confidence and provides a crucial foundation for tackling more complex mathematical concepts. They teach the fundamental principle of isolating a variable – a skill essential throughout algebra and calculus.
Successfully solving these equations reinforces the concept of inverse operations, demonstrating how to “undo” mathematical actions to reveal the unknown. This skill isn’t limited to mathematics; it fosters logical thinking and problem-solving abilities applicable to various real-world scenarios.
Furthermore, readily available resources like solving one-step equations PDF worksheets and online tutorials make practice accessible and reinforce understanding. Proficiency in one-step equations streamlines the learning process for more advanced topics, preventing future difficulties and promoting mathematical fluency.

Understanding the Basics
Equations balance mathematical statements; variables represent unknowns, while constants have fixed values. Solving involves isolating the variable using inverse operations, aided by PDF resources.
Variables and Constants
In the realm of one-step equations, understanding the distinction between variables and constants is absolutely crucial. A variable, typically represented by a letter like ‘x’, ‘y’, or ‘z’, symbolizes an unknown value – the very quantity we aim to uncover through the equation-solving process. Think of it as a placeholder awaiting its determined numerical identity.
Conversely, a constant is a fixed, unchanging numerical value. These are the numbers in the equation that remain consistent throughout. For example, in the equation ‘x + 5 = 10’, ‘5’ and ’10’ are constants. Many PDF worksheets dedicated to solving one-step equations emphasize identifying these components as a foundational step.
Recognizing this difference allows you to strategically apply inverse operations to isolate the variable and ultimately determine its value. Mastering this concept, often reinforced through practice with downloadable PDF exercises, is key to building confidence and proficiency in algebra;
The Goal of Solving Equations
The primary goal of solving equations, including the simpler one-step variety, is to isolate the variable. This means manipulating the equation – using valid mathematical operations – until the variable stands alone on one side of the equals sign, with its corresponding numerical value on the other. Essentially, we’re answering the question: “What value of the variable makes this equation true?”
Numerous PDF resources available online specifically target this skill, providing step-by-step guidance and practice problems. These materials often highlight the importance of maintaining balance; whatever operation is performed on one side of the equation must also be performed on the other.
Successfully isolating the variable provides the solution to the equation. Many PDF worksheets conclude with a verification step, encouraging students to substitute their solution back into the original equation to confirm its accuracy, solidifying their understanding.
Inverse Operations
Inverse operations are the key to unlocking one-step equations. They “undo” each other, allowing us to isolate the variable. Addition and subtraction are inverses; multiplication and division are inverses. When solving equations, we employ these inverses to move terms around and simplify the expression.
For example, to solve an equation involving addition, we use subtraction, and vice-versa. Many PDF worksheets dedicated to one-step equations emphasize mastering these inverse relationships. They often present equations with a clear indication of which inverse operation to apply.
Understanding inverse operations is crucial because it’s the foundational principle behind solving all algebraic equations, not just the simple one-step variety. Online tutorials and PDF guides frequently demonstrate this concept with visual aids and practical examples, ensuring comprehension.

Solving Equations with Addition and Subtraction
Addition and subtraction are fundamental to solving one-step equations; PDF resources often focus on these operations, building essential algebraic skills.
Solving Equations: Addition
When an equation involves subtraction, we utilize the inverse operation – addition – to isolate the variable. Numerous PDF worksheets and online resources demonstrate this process clearly. The core principle is maintaining balance; whatever operation is performed on one side of the equation must be replicated on the other.
For instance, consider an equation like x ⎼ 5 = 10. To isolate ‘x’, we add 5 to both sides, resulting in x = 15. These PDF materials often include step-by-step solutions and practice problems, reinforcing the concept. Understanding this balance is crucial.
Many tutorials emphasize showing your work, which aids in error detection and comprehension. Consistent practice with these PDF exercises builds confidence and fluency in solving addition-based one-step equations. Remember to always verify your solution by substituting it back into the original equation!
Example 1: Solving x ⎻ 5 = 10
Let’s walk through solving the equation x ⎼ 5 = 10. Our goal is to isolate ‘x’. Since 5 is being subtracted from ‘x’, we employ the inverse operation: addition. We add 5 to both sides of the equation to maintain balance. This gives us x ⎻ 5 + 5 = 10 + 5.
Simplifying both sides, we get x = 15. This is our proposed solution. Many PDF worksheets present similar examples with detailed solution steps. It’s vital to understand why we add to both sides – it preserves the equation’s equality.
To confirm our answer, we substitute 15 back into the original equation: 15 ⎼ 5 = 10. This is true, therefore x = 15 is the correct solution. Practice with similar problems found in PDF resources will solidify this skill.
Solving Equations: Subtraction
When solving one-step equations involving subtraction, the key is to utilize the inverse operation – addition. If an equation presents a term being subtracted from the variable, we add that same value to both sides to isolate the variable. This maintains the equation’s balance, a crucial principle in algebra.
Numerous PDF worksheets offer practice problems specifically designed to reinforce this concept. For instance, if you encounter an equation like y + 3 = 7, you would subtract 3 from both sides.
This yields y + 3 ⎼ 3 = 7 ⎼ 3, simplifying to y = 4. Always remember to check your solution by substituting it back into the original equation. Many online tutorials and PDF guides emphasize this verification step. Consistent practice with these resources builds confidence and mastery.
Example 2: Solving y + 3 = 7
Let’s walk through solving the equation y + 3 = 7 step-by-step. Our goal is to isolate ‘y’, meaning we want to get ‘y’ by itself on one side of the equation. Since 3 is being added to ‘y’, we’ll use the inverse operation: subtraction.
We subtract 3 from both sides of the equation to maintain balance: y + 3 ⎼ 3 = 7 ⎼ 3. This simplifies to y = 4.
To verify our solution, we substitute y = 4 back into the original equation: 4 + 3 = 7. This is a true statement, confirming that y = 4 is the correct solution. Many PDF worksheets provide similar examples for practice. Online resources and PDF guides often demonstrate this verification process, reinforcing the importance of checking your work;
Solving Equations with Multiplication and Division
Multiplication and division equations require applying inverse operations to isolate the variable, mirroring addition and subtraction techniques.
PDF resources and tutorials offer practice!
Solving Equations: Multiplication
When faced with an equation where a variable is being multiplied by a constant, such as 3a = 15, the key to solving lies in utilizing the inverse operation – division. To isolate ‘a’, we divide both sides of the equation by 3. This maintains the equation’s balance, ensuring the solution remains accurate. Therefore, 3a / 3 = 15 / 3, which simplifies to a = 5.
Numerous online resources and printable PDF worksheets provide ample practice opportunities for mastering this skill. These resources often include step-by-step solutions and detailed explanations, catering to various learning styles. Remember to always check your answer by substituting the solved value back into the original equation to verify its correctness. Consistent practice with these resources will build confidence and proficiency in solving multiplication equations.
Understanding this fundamental principle is crucial for progressing to more complex algebraic concepts.
Example 3: Solving z / 2 = 4
Let’s walk through solving the equation z / 2 = 4. Here, the variable ‘z’ is being divided by 2. To isolate ‘z’, we must apply the inverse operation: multiplication. We multiply both sides of the equation by 2, maintaining balance. This gives us (z / 2) * 2 = 4 * 2, which simplifies to z = 8.
To confirm our solution, we substitute z = 8 back into the original equation: 8 / 2 = 4. This is a true statement, verifying that z = 8 is the correct solution. Many PDF worksheets available online offer similar practice problems, allowing you to reinforce this skill.
Remember, consistent practice is key to mastering one-step equations and building a strong foundation in algebra.
Solving Equations: Division
When an equation presents a variable being multiplied by a number, we employ division to isolate the variable. This is the inverse operation of multiplication, ensuring we maintain equation balance. For instance, consider an equation like 4x = 20. To solve for ‘x’, we divide both sides by 4, resulting in (4x) / 4 = 20 / 4, which simplifies to x = 5.
Always remember to perform the same operation on both sides of the equation to preserve equality. Numerous online resources and PDF worksheets provide ample practice with division-based one-step equations.
These resources often include answer keys for self-assessment, aiding in skill development and confidence building. Consistent practice is crucial for mastering this fundamental algebraic concept.
Example 4: Solving 3a = 15
Let’s walk through solving the equation 3a = 15 step-by-step. Our goal is to isolate the variable ‘a’. Since ‘a’ is being multiplied by 3, we’ll use the inverse operation: division. We divide both sides of the equation by 3 to maintain balance. This gives us (3a) / 3 = 15 / 3.
Simplifying this equation, we find that a = 5. To verify our solution, we substitute 5 back into the original equation: 3 * 5 = 15, which is true. Therefore, a = 5 is the correct solution.
Many PDF worksheets offer similar examples for practice, reinforcing this crucial skill. Remember to always check your answer!

Checking Your Solutions
Verification is vital! Substitute your answer back into the original equation to confirm its validity, ensuring accuracy and solidifying understanding.
The Importance of Verification
Verification isn’t merely a procedural step; it’s a cornerstone of mathematical accuracy and a crucial habit to cultivate when solving one-step equations. After arriving at a potential solution, substituting it back into the original equation allows you to definitively confirm whether it satisfies the equation’s conditions.
This process acts as a self-check, catching potential errors in your calculations or application of inverse operations. A mismatch between the left and right sides of the equation indicates a mistake somewhere in your solving process, prompting you to revisit your steps.
Utilizing PDF worksheets for practice reinforces this habit, as many include dedicated spaces for solution checking. Ignoring verification is akin to building a structure without ensuring its foundation is sound – it risks collapse. Consistent verification builds confidence and a deeper understanding of equation solving principles.
How to Check Your Answer
To effectively check your solution when solving one-step equations, carefully substitute the value you’ve found for the variable in the original equation. Then, simplify both sides of the equation independently, following the order of operations.
If both sides evaluate to the same numerical value, your solution is correct! This confirms that your chosen value truly satisfies the equation. If the values differ, an error occurred during the solving process, and you must re-examine your steps.
Many PDF worksheets dedicated to practicing these equations include answer keys, allowing for immediate self-assessment. Remember, checking isn’t about finding the ‘right’ answer; it’s about validating the process and solidifying your understanding of algebraic principles.
Example 5: Checking the Solution to 2b + 1 = 9
Let’s verify the solution to the equation 2b + 1 = 9. First, we solved for ‘b’ and found b = 4. Now, to check, substitute 4 back into the original equation: 2(4) + 1.
Simplifying the left side, we get 8 + 1 = 9. The right side of the original equation is already 9. Since both sides equal 9, our solution, b = 4, is correct!
Many PDF practice resources for solving one-step equations emphasize this verification step. Consistent checking builds confidence and reinforces the understanding that a solution must satisfy the initial equation. This process is crucial for avoiding errors and developing strong algebraic skills;
Real-World Applications
One-step equations model everyday scenarios, like calculating costs – a cookie costing $0.95, with a total spent of $12.35, as seen in PDF examples.
Word Problems Involving One-Step Equations
One-step equations frequently appear disguised as word problems, requiring translation from everyday language into mathematical expressions. These problems build crucial problem-solving skills, bridging the gap between abstract algebra and practical applications.
For instance, consider scenarios involving costs, quantities, or distances. A common example, often found in practice PDFs, involves determining the number of items purchased given a total cost and the price per item.
Successfully solving these problems demands careful reading, identifying the unknown variable, and formulating an equation that accurately represents the given information.

The ability to translate words into equations is a cornerstone of mathematical proficiency, and mastering one-step equations provides an excellent starting point for developing this essential skill. Practice with varied word problems, utilizing available resources like worksheets, is key to building confidence and fluency.
Example 6: Cookie Cost Problem (Based on provided text)
Let’s tackle a real-world problem: Kirra spent $12.35 on cookies at a school coffee house, where each cookie costs $0.95. We want to determine how many cookies Kirra purchased.
Let ‘c’ represent the number of cookies. The equation is 0.95c = 12.35. To isolate ‘c’, we perform a division operation. Dividing both sides by 0.95, we get c = 12.35 / 0.95.
Calculating this gives us c = 13. Therefore, Kirra bought 13 cookies. This example demonstrates how a simple one-step equation can model a practical scenario.
Many PDF worksheets offer similar problems for practice. Remember to always define your variable, set up the equation, and utilize the inverse operation to solve. Checking your answer by multiplying 0;95 by 13 confirms the total cost of $12.35.

Resources and Practice
One-step equation worksheets in PDF format are widely available online, offering focused practice. Complement these with helpful video tutorials for enhanced understanding.
One-Step Equation Worksheets (PDF)
Numerous websites provide free, printable one-step equation worksheets in PDF format, catering to various skill levels. These resources are invaluable for reinforcing concepts learned and building confidence in solving simple algebraic equations.
Typically, these worksheets present a series of equations requiring students to isolate the variable using inverse operations – addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division. Many PDFs include answer keys, enabling self-assessment and immediate feedback.
Look for worksheets that progressively increase in difficulty, starting with basic addition and subtraction problems and gradually introducing multiplication and division. Some worksheets also incorporate word problems to apply these skills in real-world contexts.
Searching online for “one-step equations worksheet PDF” will yield a wealth of options. Remember to preview the worksheet to ensure it aligns with the specific concepts being practiced. Printable documents offer a convenient and accessible way to supplement classroom learning or provide extra practice at home.
Online Video Tutorials
For learners who benefit from visual explanations, a plethora of online video tutorials are available to guide them through solving one-step equations. Platforms like YouTube host countless videos demonstrating the process step-by-step, often featuring worked examples and clear explanations of inverse operations.
These tutorials can be particularly helpful for students struggling with specific concepts or those who prefer a more dynamic learning experience. Many videos also address common mistakes and provide tips for avoiding them.
Searching for “solving one-step equations tutorial” will reveal a range of options, from short, focused explanations to more comprehensive lessons. Some videos even incorporate interactive quizzes or practice problems to reinforce learning.
Supplementing worksheet practice with video tutorials can create a well-rounded learning approach, catering to different learning styles and ensuring a thorough understanding of the fundamental principles.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Incorrectly applying inverse operations and forgetting to check solutions are frequent errors when solving one-step equations; careful practice prevents these!
Incorrectly Applying Inverse Operations
A common pitfall when solving one-step equations involves misapplying inverse operations. Remember, the goal is to isolate the variable. If an equation presents addition, subtraction is the inverse, and vice-versa. Similarly, multiplication and division are inverse operations of each other.
Students often mistakenly add when they should subtract, or multiply when division is required. This leads to an incorrect solution. For example, in the equation x + 5 = 10, subtracting 5 from both sides is the correct inverse operation, not adding.
Carefully identify the operation being performed on the variable and then select the corresponding inverse operation. Utilizing PDF worksheets for practice can reinforce this concept. Double-checking your work and understanding the fundamental principles of inverse operations are crucial for success. Always prioritize accuracy over speed!
Forgetting to Check Your Solution
A frequent error students make when solving one-step equations is neglecting to verify their answer. After arriving at a potential solution, it’s vital to substitute that value back into the original equation. This confirms whether the solution truly satisfies the equation’s conditions.
Checking involves evaluating both sides of the equation independently with the substituted value. If both sides yield the same result, the solution is correct. If they differ, an error occurred during the solving process, requiring re-evaluation.
Many PDF worksheets dedicated to equation solving emphasize this crucial step. It’s a safeguard against arithmetic mistakes or incorrect application of inverse operations. Developing a habit of verification builds confidence and ensures accuracy. Don’t skip this final, essential step!